Transform Fats in Your Allies to Keep in Shape and Healthy
Most of the people think fats are the enemy, but the truth is, just like carbs and proteins, fat is a macronutrient your body needs. In addition, when you consume fats with moderation, you can get good results.
Fats are high in calories, but in according amounts. Besides, they help improving corporal composition and health. For instance, he key to eating the correct type of fat is choosing natural sources of it and moderating portions.
We have to control portions. When we consume fat in huge quantities, this can lead to weight gain. Subsequently, when fat intakes become regular,this can progress into obesity. The chance of other serious health situationslike heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers, are linked to obesity.
All kinds of fat afford an equal amount of calories (9kcal per gram). The amount of calories is higher than other nutrients, like protein and carb, which cover about 4 kcal per gram.
Again, what you can control is the quality and quantity of nutrients you consume. In short, to choose wisely you must know types and all the information you need about fats.
What are The Types of Fats?
Fatty acids are the structures bounded to form fats molecules. To sum up, according to the number of fatty acids chains, the length of the chains and number of hydrogen atoms, fats have different structures, form, and functions.
Trans fats, polyunsaturated and monosaturated fats, and saturated fats are the types of fats we must know. The number of hydrogen atoms is crucial to classify fats.
Trans Fats (Bad)
Industries make a process called hydrogenation to some liquid oils to make them solid and to prevent them from turning into rancid. Consequently, this process permits trans fats formation. Moreover, trans fats increase LDL cholesterol levels and reduce HDL cholesterol levels, allowing cholesterol plaques formation in vessels.
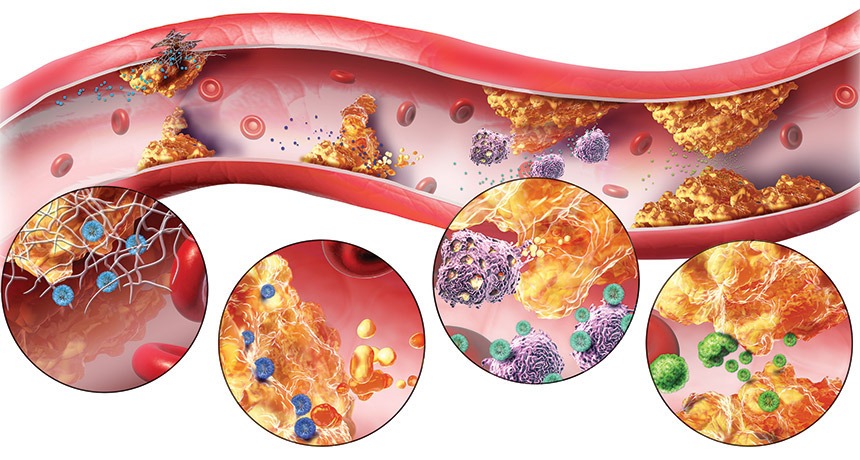
As a result, consuming trans fats regularly produces harmful consequences to our health, like:
- Inflammation
- Heart diseases
- Stroke
- Diabetes
- Insulin resistance
You can find trans fats in products like processed foods, snack foodslike chips, margarine, cookies and foods made with shortening and partly hydrogenated oils.
They also are formed when vegetable oils are boiled and reheated to fry foods at elevated temperatures. For this reason, fast foods and takeaway foodsare high in trans fats.
Saturated Fats (In-Between)
Saturated refers to the number of hydrogen atoms inthe molecule. As result, it’s saturated with hydrogen. Saturated fats drive up total cholesterol, elevating LDL cholesterol, which brings consequences to arteries, similarly to trans fats. For this reason, experts recommend saturated fats intake to be lesser than 10%.
This fat is solid at room temperature. On the other hand, saturated fats are in dairy products like butter, full-fat milk, cheese, cream,cooking margarine, palm oil, chicken skin, processed meats like pepperoni, fatty cuts of beef and pork, and many others.

Different studies haven’t coincided whether saturated fats increase heart disease risk or not. Nevertheless, what is true is that substituting saturated fat with polyunsaturated fats like vegetable oils or high-fiber carbohydrates is the greatest bet for decreasing the heart disease risk. However, substituting saturated fat with very processed carbs could do the contrary.
In short, they always conclude to avoid this type of fat.
Unsaturated Fats (good)
These fats have lesser hydrogen atoms quantity. In addition, they usually come from nuts, vegetables, seeds, and fish. In addition, they can be monounsaturated or polyunsaturated.

Monounsaturated Fats
The structure of monounsaturated fats is liquid at room temperature. For instance, good sources of monounsaturated fats are peanut oil,olive oil,avocados, canola oil, and most nuts. Specialists recommend monounsaturated fatsover saturated and trans fats.
Polyunsaturated Fats
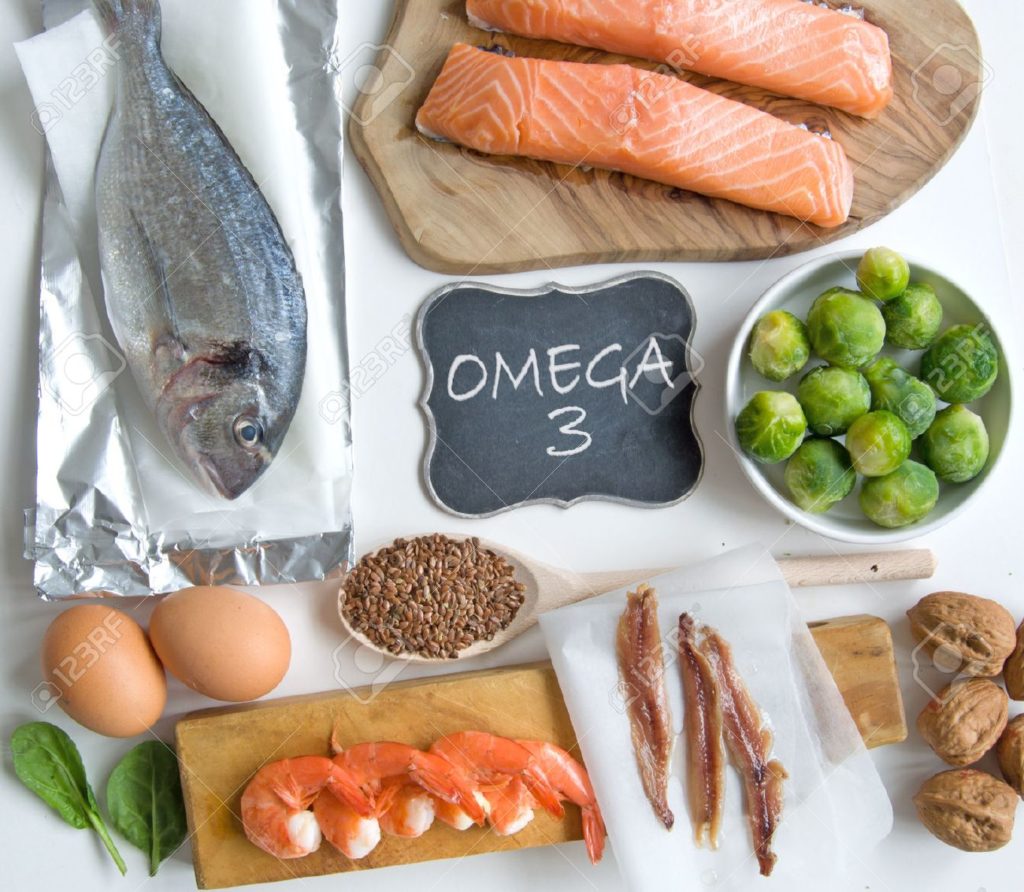
Essential fatty acids are fats we must obtain from foods because ourbody doesn’t produce them. As result, polyunsaturated fats are essential fats, being omega-3 and omega-6 the two main types. For example, fish, sardines, flaxseeds, nuts and linseed ground seeds are some sources of omega-3.
The organism uses essential fatty acids to produce hormones and build the lipid cape of cells. I addition, all of these processes improve signalization and insulin sensitiveness. For instance, this improvement allows a better metabolic function, fat burning, and muscle growth.
In addition, replacing saturated fats and refined carbs with poly- and monounsaturated fats reduces LDL cholesterol levels.
Benefits of consuming Omega-3
- Your metabolism speeds up. An optimum omega-3 intake increases lipolysis or fat oxidation because it “turns on” fat burning genes and “inhibit” lipogenesis stimulating genes (accumulation).

- Reduces insulin resistance.
- Lows glucose in blood and improves insulin sensitiveness.
- Assists muscle mass growth.
- Improve your mood and relieves depression. Your brain is made, basically, of cholesterol and fat. Therefore, the best fat for the brain is Omega-3 like salmon, nuts, fish oil, sardines, and others.
- Decreases inflammation and cancer risk.
- Hair and skin will look better.
- Avoid arteriosclerosis.
- Helps controlling appetite and anxiety.
- Increases oxidation, stimulating fat burning.
- Betters arthritis symptoms. They may help decrease thedemand of corticosteroid medication in if you have this condition.
A good idea to improve omega-3 intake is to add supplements to your diet. Try to add omega-3 capsules and eating 1 to 2 g per day with some food. If you’re looking for losing corporal fat, you should consume fats with proteins, vegetables or fruits instead of starched complex carbs.
Why are Fats so Important?
Fats have many important roles in our organism:
- Improve your corporal composition.
- Give you energy.
- When you low your carbs ingest and upsurge good fats intakes, your insulin sensitiveness gets better.
- Protect your organs.
- A diet with great good fats intake enhances hormonal balance, elevating testosterone and growth hormone levels.
- Decreases cholesterol and triglycerides levels. Studies confirm a diet with fat is not always the one that elevates triglycerides but a diet with high refined carbs intake.
- Good fats optimize glucose use in the organism.
- Is better a diet with high proteins intakes, moderated fats and low in carbs than low fat and high carbs diet. As a result, metabolic adaptation is better when you consume higher levels of good fats and control, not eliminate, carbohydrates.
- Helps to control appetite, principally when you combine it with protein. The effect is better if fat comes from coconut oil.
- Improve your hormonal balance
- Fats are essential to absorb some vitamins.

Having this information clear, you’ll be capable to choose your fat sources wisely. In conclussion, knowing how your organism acts is the better tool you could have to give it the better sources it needs to function properly.